
Written by Justin Zzyzx – Author of “Rockhound Barstow”
This location and many others are featured in the field guide – Click here to buy a copy for yourself
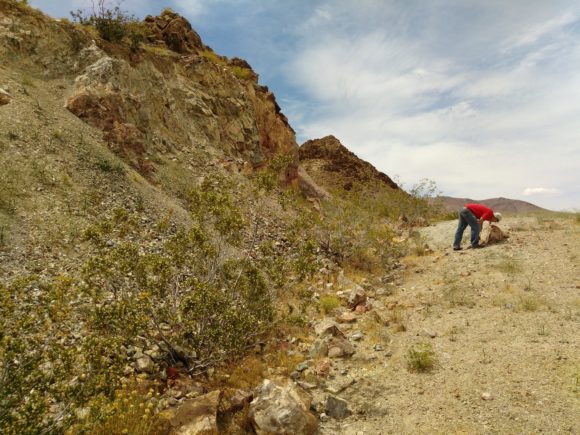

Justin Zzyzx inspecting boulders at the Noble Prospect.
I just love exploring the nooks and crannies of the hills and mountains around Barstow California. The area around here is known for the beautiful geological formations all around, such as Rainbow Ridge, as well as the silver mines of Calico, once a silver boom town, now a commercial tourist attraction. Barstow, a perfect place to set up base and explore the Cady Mountains, Afton Canyon, Opal Mountain, Mule Canyon, Alvord Mountain, Yermo’s rolling hills of alluvial agates and jaspers and so much more. There is a veritable treasure chest of mineral adventures to be had in these colorful hills, visiting is a thrill, and I, as a resident, love to take full advantages of these rock deposits.
As a frequent leader of field trips and author of the “Rockhound Barstow” field guide, I’m always looking for new places to take people to collect interesting minerals and lapidary materials. My personal favorite is finding places where there are both nice crystallized minerals, as well as colorful lapidary material, that way, out of the dozens of rockhounds who have joined me over the past year on each monthly field trip, everybody is happy with what they can find. Exploring mining information on MRDS.org, I noticed several mines located in the Northern parts of the Calico mountains. I could see, just 10 miles away from my pistachio grove I call home in Newberry Springs, there was a Wollastonite mine, a Nickel mine and an Arsenic mine, all bunched up to the West of Coyote Dry Lake.
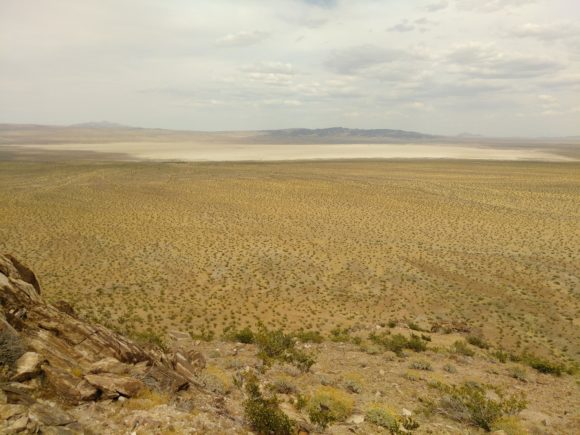

View looking out to Coyote Dry Lake from the un-named Nickel deposit
On our first outing to this string of locations we tried to access it from the East, coming up Coyote Dry Lake road. The dry lake was not as dry as we expected, in fact, it was quite moist and with no desire to go “muddin”, we turned back and tried the other way into the area, all the way around the Fort Irwin road passage, 20 miles to the West. Fort Irwin road is a VERY busy two-three lane road that connects Fort Irwin to Barstow and highway 15. Fort Irwin, a large Marine base, requires a large amount of workers from the Barstow area to work the service industry jobs, as well as the tech jobs, along with all the contractors, you can imagine this is a very busy road. We drove through the pass on the West side, looking at all the remains from the silver mines that made the Calico district what it was and what it is today. The ore was mostly chloragyrite, a silver mineral that is toxic to process, proving to be costly and environmentally unsound, so, the silver mines stand dormant, forever.
Entering on Madrugador road, Eastbound from Fort Irwin road, you pass by a Wollastonite deposit to the North, which we inspected with little of interest to be found, then, continuing along on this fairly smooth, slightly rocky road we turned off to the Northeast on a power line road which then takes us directly to the Wolly Wollastonite #5 deposit, a long abandoned deposit of this interesting white mineral. Some field guides have published this location, however, they always refer to it as an Onyx deposit. Onyx, a name for Calcite, is found at lots of places around the Calico mountains, however, at this deposit, there is only the non-stop white bliss of massive Wollastonite.
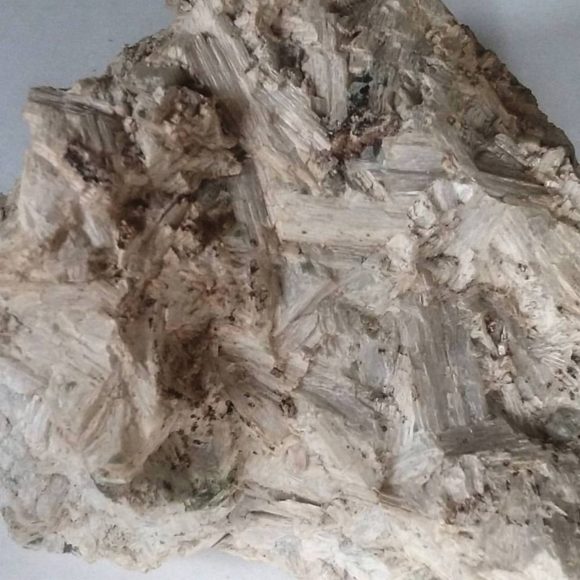

Long fiber Wollastonite crystals on the surface of massive Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a mineral that can be found as part of a Skarn deposit. Common related minerals are Grossular Garnet, Calcite, Quartz, Hedenburgite, and Epidote. The grains of the skarn deposits can be quite dense, leading to amazingly hard stones that can be worked into lapidary objects like vases and pillars. The wollastonite here was most likely mined for use in the pottery industry. Wollastonite, CaSiO3, a Calcium Silica Oxygen mineral that often has impurities of iron, manganese and magnesium, all elements found in abundance across this mountain range. Crushed, this powdered rock would be used for adding to clay, reducing cracking when ceramics are fired in a kiln, as well as added to paint base, a filler to make paint thicker.
At the Wolly Wollastonite deposit we would find tons of massive white wollastonite with the choice mineral specimens being the small bits and thin plates of acicular “long fiber” wollastonite crystals, which form flat on the surface of the rocks and boulders. Along with these, a bit of orange Grossular garnet can be found forming in the sharp borders between the wollastonite and the county rock. Finding larger pieces of this material is uncommon, but possible, however bits of wollastonite with thin areas of garnet are fairly common along the waste rock piles. In the quarried areas, along the rock wall, you can see several veins of garnet, but, in my opinion, they are not terribly thrilling. One thing is for sure, the guides that have continuously pegged this as an Onyx deposit can now be corrected in the next printing! The deposit takes up the Northern side of this far outlying mountain, spilling out of the most Northern part of the Calico mountains. Various bits and smears of other minerals have been spotted, like epidote and hedenburgite, so with further exploration you might uncover something interesting.
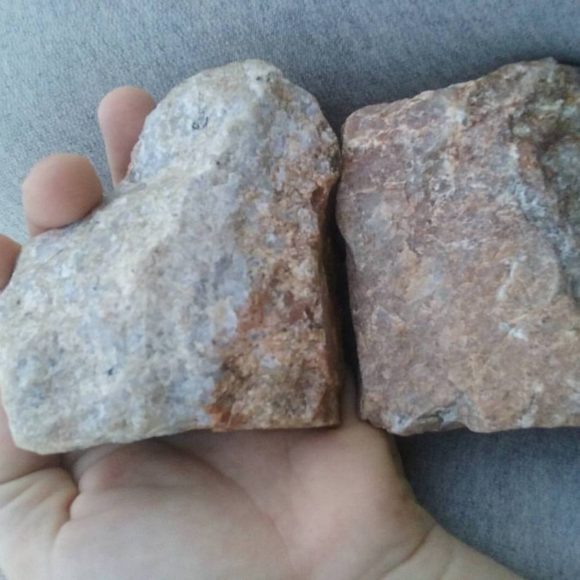

Spessartine garnet masses found in conjunction with the wollastonite deposits of the North Calico Mountains
A few months before I decided to visit this Wollastonite deposit, I was told by a gold miner in the Hesperia area that there was a Wollastonite deposit up in the North Calico mountains that had terminated grossular garnets. Wollastonite forms as a part of skarn deposits. One of the best mineral deposits in these formations are calcite pods with glossy grossular garnets underneath. Locations around the world produce specimens like this, the calcite acts as a blanket for the garnets, protecting them from any harm, until we, rockhounds, remove them from the ground and soak them in acid to dissolve the calcite and reveal the beautiful garnets underneath. While massive garnet is found at the Wolly Wollastonite deposit, the lack of calcite pods at this and every other Wollastonite deposit I’ve visited has turned up fruitless. Yet, chasing this lead has brought me to explore some infrequently visited areas of the rocky desert hillsides.
Going back in reverse from the Wollastonite deposit, you can head South in the first turn, which is a wash that leads up to the solid hillside and upwards on a road that leads to a former Nickel deposit, resting on this craggy spire, a semi steep climb leads to a non-connecting circular road around the peak. From here you have spectacular views of the valley below, the vast white/tan of Coyote Dry Lake, the Coptic monistary, and hey, I can even see my house from up here! Looking at this location from the comfort of my home, with my imported mine marker data from MRDS, I could see this Nickel mine and also find out more information about it. It referenced a mention in a a Southern Pacific Railroad booklet on Mineral of Industry, Volume 3, which mentions the deposit geology as “niccolite, arsenopyrite, annabergite, and uvarovite in a verticle silicic dike that strikes NE along a shear zone in hornfels and quartzite.”
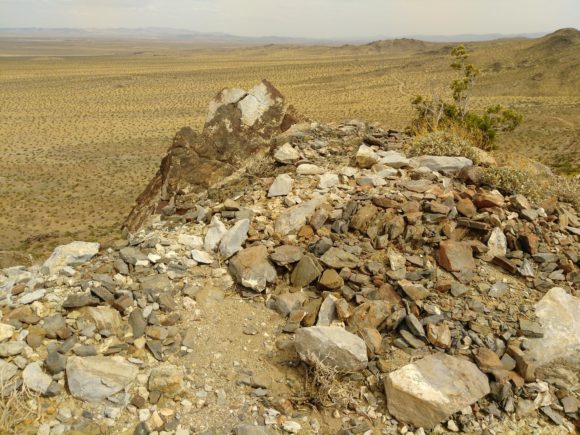

View from on top of un-named Nickel deposit
Off we went, to go visit the un-named nickel deposit. The wind on our first visit makes the location very memorable. We can have wind gusts over 65 miles an hour on some days around these parts and that day the wind was so forceful we were quite worried we would be swept off the mountain. Maintaining a tight foothold, we explored the area, looking for bright green crystals of annabergite and chrome green uvarovite garnets. Instead, we found the meaning of “silicic dike”! All of the minerals we have found at this location have been frozen in blocks of silica. While this does not do anything for us mineral collectors, it makes for a unique lapidary material. The same stuff as the classic German “Nickel Quartz”, this green stone takes a nice polish and the contrast of white and green makes for an interesting stone. Floating around in this silica, tiny bits of chrome green uvarovite garnet are found, while nothing to write home about, they do add a little something to some of the slabs and tumbled stones we produced out of this ore. If there were crystals here, this could be one of my favorite locations, but even in massive lapidary form, this in a rare treat in terms of mineralogy, a geat view-point in this area of the North Calico mountains and yet, just one of many locations in a short distance in this mountain range.
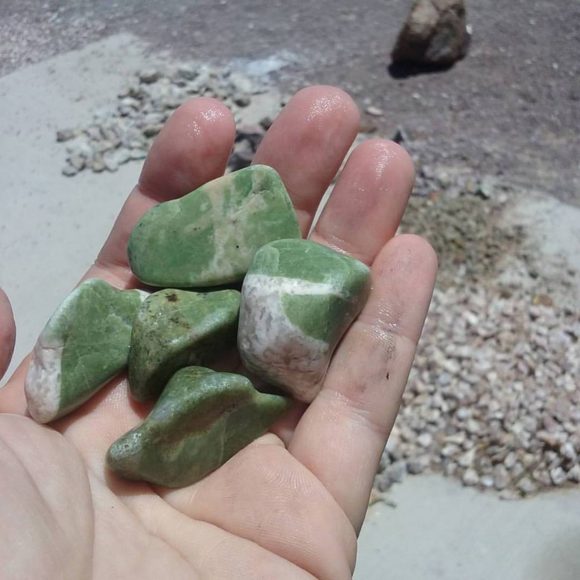

Tumbled nickel quartz from the un-named Nickel deposit
Just off to the Southwest, the road takes you to the Puerto Negro mine, a series of rock dumps that stop at a mine entrance a few hundred yards south of the beginning of the dumps. This is an Arsenic mine that produced an arsenic rich ore with the occasional bit of calcite and realgar. While I have not found many specimens at this location, the few I have found have been quite uncommon, orangy red realgar in layered clear calcite crystals. Drive North to connect back with the power line road and drive over to the next canyon to the South, taking Madrugador Road, home to several prospects for copper and gold, before heading back out to Fort Irwin Road. These gold deposits do not have much in the way of collectables for mineral or lapidary enthusiasts, however, they do produce chunks of calcite and masses of red, iron stained, quartz.
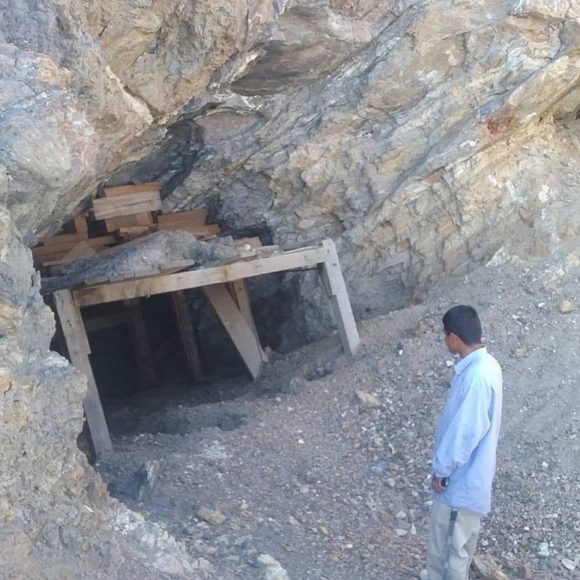

Entrance to the Arsenic Mine, the Puerto Negro
From here, it is time to go across Ft. Irwin Road, just a few hundred yards to the South, a road stretches out towards the Northwest, reaching out to several locations were crystals and lapidary materials can be found. The road is a very nice, mostly smooth flat desert dirt road. There are a couple tiny washed out areas, but most any passenger car can navigate the area. Immediately to the North, a small set of ridges spread out, the ridge to the West of the hills contains two locations to explore. A massive Barite locality called the Ball mine and a funky Wollastonite deposit with some odd rocks to be found. You pull off this new dirt road and into a wash road that loops around, park here and hike into the mountain valley to find the Ball mine, which is easy to see and high up on the hillside.
The Ball mine was a series of tunnels and surface workings that produced massive white barite, which can be found in abundance as lumps of heavy white rock. While unassuming, when exposed to UV light, these lumps glow a pleasing green and pink. There are tons and tons of this material laying around the mine adits, so you will have plenty to choose from. Continuing North into the canyon you will come across a Wollastonite deposit that has bits of calcite and some black rock that is said to be chromium bearing.
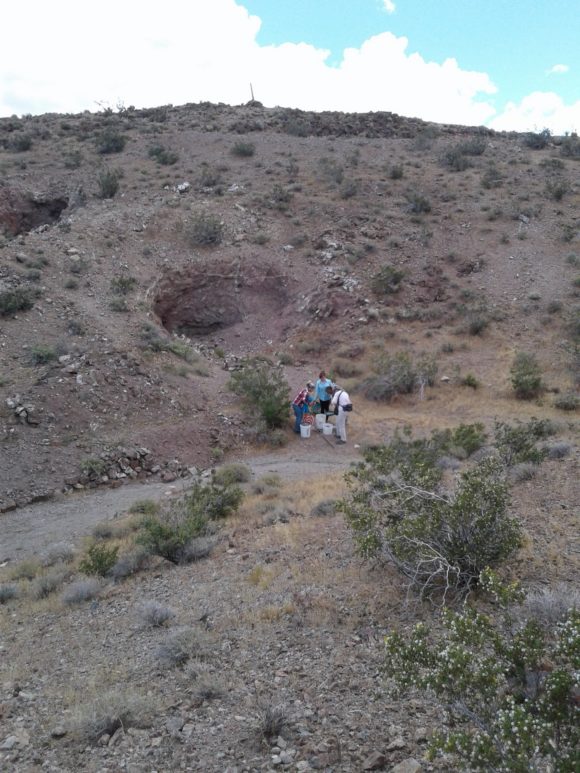

Rockhounds collecting Garnets at the Nobel Prospect
Back on the main dirt road, you continue Northwest for a mile or so until you come across a faint road headed South which leads to a large pile of rocks in the middle of the flat desert. It is unusual to see a pile of rocks such as this, however, this outcropping of rock is a happy accident for all of us. Here you can find a great deposit of Onyx, a flowing series of banded tans and yellows, along with bright red caused by iron impurities, along with areas of quartz, in the center of the stones as well as on the surface. Druzy specimens of quartz and calcite can be found, the only drawback is the size of the matrix they are sometimes attached to! The large chunks of stone cut to reveal beautiful patterns, while being nice and crack free, solid cutting material. It is remarkably easy to find, within a half hour at the location, cutting material to keep you occupied for days and weeks.
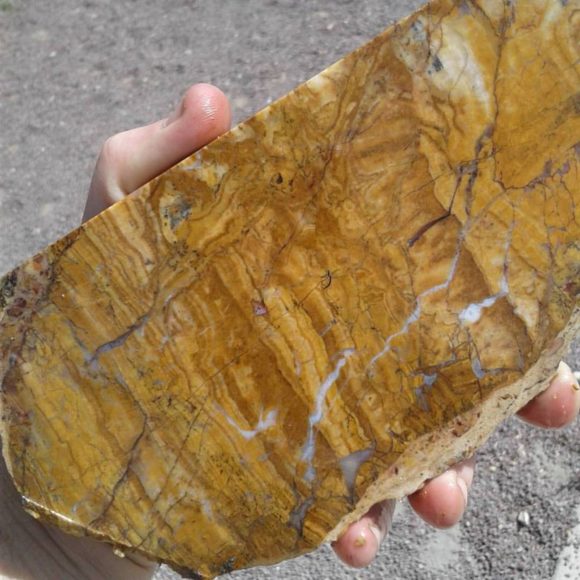

Sliced Travertine from the large travertine outcrop in the North Calico Mountains
Traveling only another thousand yards to the West along the main dirt road, you come across the Noble prospect, a mineralized zone consisting of a short canyon wash to the East, with short adits that pushed out garnets, quartz, epidote and calcite. While we were hoping for garnets trapped inside calcite pods, these garnets are frozen in a quartz matrix, an while crystals can get up to an inch across in size, there is no way to free them from the host rock. Still, terminated garnets can be found in this area and the masses of quartz, epidote and garnet make for interesting lapidary materials. Just a short distance from this wash, a road takes you a few hundred feet to a bench in the mountainside, filled with boulders containing calcite crystals and quartz druzy, the druzy areas measuring up to and over one foot in size on several of the boulders. The trick is to find specimens that are small enough to take home. Several pieces showed evidence of layers of quartz covering and replacing the calcite crystals, which make for very interesting mineral specimens.
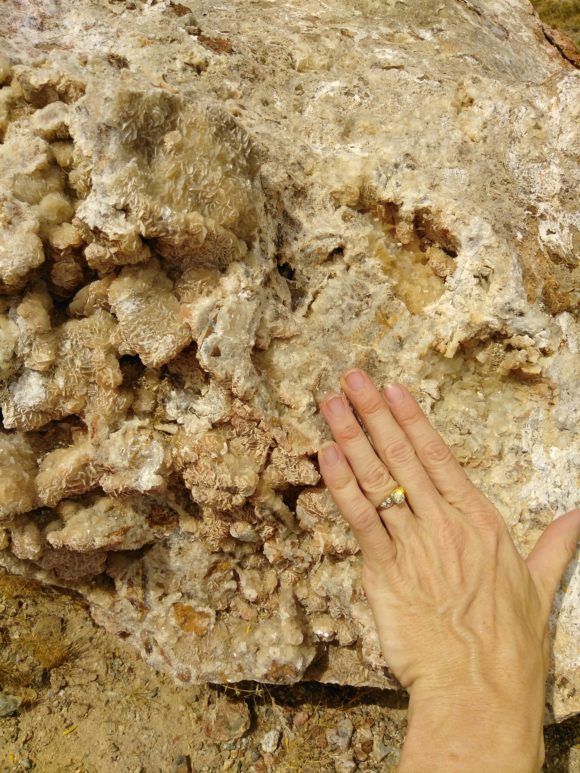

At the Noble Prospect, Boulders of Calcite with Crystals growing in vugs can be found.
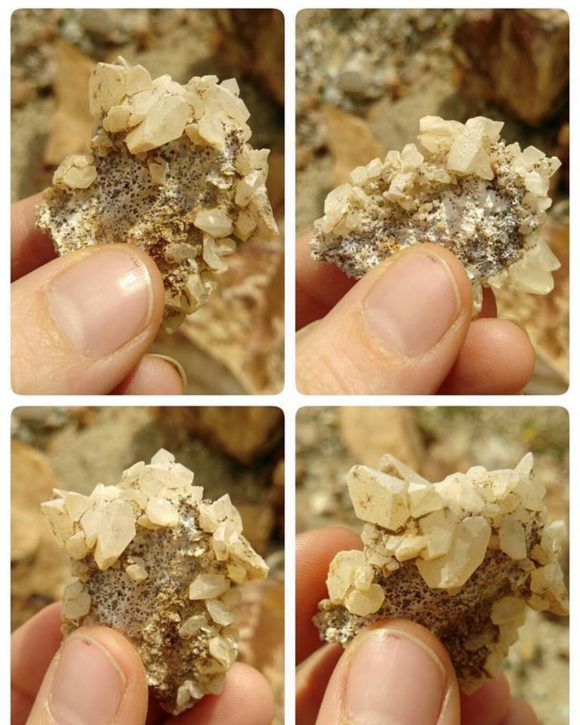

Calcite crystals plucked from the walls of the Noble Propsect.
If you like this article, check out the 28 page full color field guide “Rockhound Barstow” for sale online at the following links
Buy it on eBay
Order it on Amazon, or Buy it for Kindle eBook Readers
Or, hey, here is the map…
![]()
Cummingtonite – We know you were looking for iron rich amphiboles…

As mineral collectors on the internet know, the jokes can often lead back to one mineral.
Cummingtonite. Eliciting snickers in a room of freshmen geologists (and honestly, still getting chuckles from aged field geologists under the right conditions). Lately it is the most popular iron rich amphibole mineral to be searched for on Google. We all know when we see that fact it is not because people are looking for their favorite ugly brown rock! Most minerals are searched for their beauty, this mineral can only claim its name as the claim to fame.
Cummingtonite is a rather uncommon mineral, hailing from the riverside on the far western edge of Cummington, Massachusetts. Here is a sample of the mysterious brown crusty amphibole they were mining. Scratching their heads, someone noticed this as an unknown mineral and dubbed it Cummingtonite, in honor of the town it was found. This is often the case, such as Elbaite, Annabergite, and Boleite.
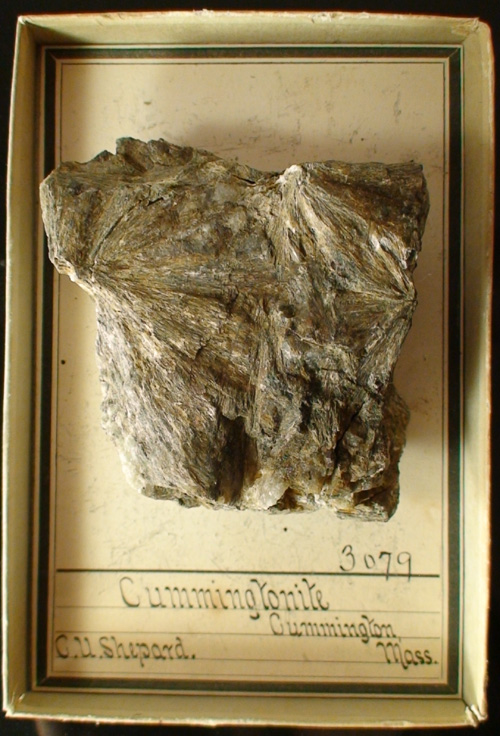
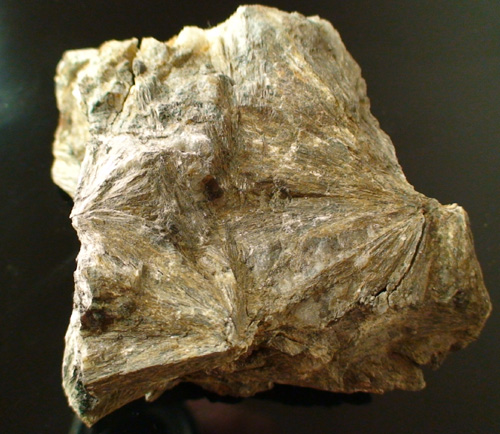




This specimen pictured is from the Philadelphia Academy of Natural Sciences. It shows a chunk of brown radiating crystals with embedded garnets. Donated by a prominent American Mineralogist Charles Upham Shepard, a man who submitted the approvals for Danburite, Microlite and others. He had one of the largest collections of minerals in the United States, donating specimens to various museums in life and death. He was a well respected lecturer on subjects of Natural History. Charles Upham Shepard graduated from Amherst College in 1924, the same year that Cummingtoite was accredited.
1824. Cummingtonite. (Dewey.)
“I have here given this name to a mineral found by ‘Dr. J. Porter in
Cummington. It appears to bo a variety of epidote. Its color is gray,
sometimes with a faint reddish tinge, unless when acted on by the
weather, when its color is yellowish. It is in distinct prisms, with oblique
seams like’ zoisite, and in radiated or fascicled masses, which are com-
posed of slender prisms. Luster somewhat shining or pearly. It is nearly
as hard as quartz, and sometimes makes a slight impression upon rock
crystal. Before the blowpipe it blackens, and a small portion melts, when
the heat is very great, into a black slag, which ik attracted by the mag-
net. With quartz and garnet .it forms a largo mass in Cummington.”
C. Dewey : Geol. Min. Mass.; Am. Jour. Sci., 1st series, Vol. VIII, p, 59.
1824. Cummingtonite. Lies by the roadside in the east part of
Cumnimgton.
Known to the common people for several years under the name.of copperas
rock; occasionally used in dyeing as a substitute for sulphate of
iron.
J. Porter: Min. Loc.; Am. Jonr. Sci., 1st series, Vol. VIII, p. 233.
Cummingtonite, the inspiration for snickers, memes and lame t-shirts, has a much more benign beginning!
With your knowledge of what Cummingtonite is, beyond a cleaver play on words, now I will tell you how you can go collect your very own specimen, along with brightly colored Lepidolite mica, UV reactive opal hyalite and shiny Hematite crystals. Far off in the desert of Arizona, nobody will hear your terrible off color humor besides your collecting partners. If you’ve ever been collecting petrified wood with a group of geologists who loudly exclaim “I’VE GOT WOOD!”, you have an idea of what to expect.
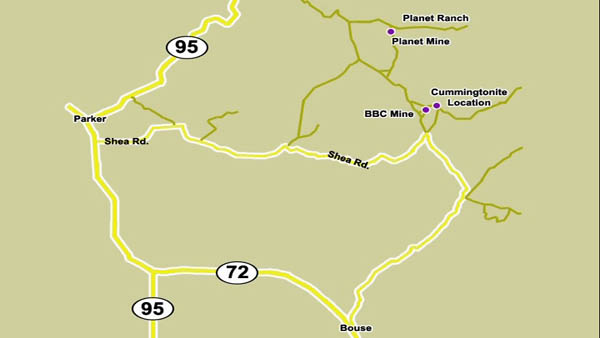
The location to collect Cummingtonite is just off to the north of the BBC Mine, a half hour away from Parker, Arizona.
The area is a wonderland of mineral collecting, with the BBC mine area boasting FINE crystals of Hematite, sometimes assosicated with Chrysocolla. Further to the North is the Planet area, filled with Barite, Malachite, Chrysocolla and all sorts of beautiful minerals. Fluorite, Gold and more copper minerals are found within 20 miles of this location, so beyond the oddball amphibole Cummingtonite, there are plenty of reasons to visit this area!
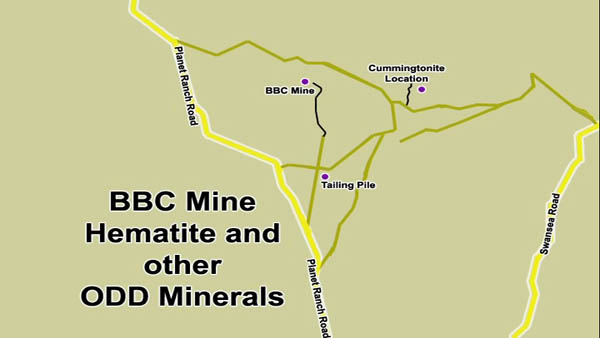

The location is a simple series of trenches, where you can find a very odd form of Lepidolite, normally known as being bright purple, here it is yellow. The hematite at the cummingtonite location is not nearly as nice as the hematite at the BBC mine. <---click to view photos on MinDat.org

The material from here is not even a tenth as nice as the crunchy material from Massachusetts, however, being able to collect your own specimen of this odd, uncommon material, is something to get excited about! 😉
If you would like a more “in-depth” view into this collecting location, let me advise you to check out the excellent Android App that will guide you to several locations around the Quartzsite/Parker area. Download this Android App for $4.99
We love you readers so much that we provided a google map pointing you to the locations.
View Cummingtonite and BBC Mine in a larger map
And I’m not completely innocent on the juvenile jokes…I am the proud owner of a Dickite specimen from Beaver Creek. 😉

